

The differential for a patient presenting with localized pain in the area of the pes anserine bursa is broad. The pes anserine bursa lies directly beneath the tendons at their insertion. With knee flexion to 90 degrees, tenderness may be palpated along the medial tendinous structures of the pes anserine group as they travel to insert along the medial tibial region.
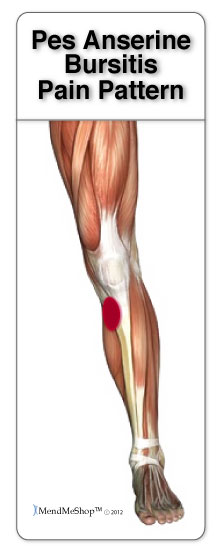
Tenderness will likely be present in the medial knee joint and may extend along the proximal, medial tibial region.
Pes anserine muscles full#
On physical examination, the affected knee should initially be evaluated in full extension. Swelling may or may not be present. In patients with osteoarthritis, the clinician should have heightened suspicion for the possibility of pes anserine pain. The semitendinosus, gracilis, and sartorius function in unison in the act of crossing one leg over the other thus, this motion typically will elicit the pain seen in pes anserine bursitis.Īdditionally, there may be subjective complaints of muscle weakness and decreased range of motion of the knee joint. Tenderness is invariably present over at the insertion of the pes anserine tendons, “goose’s foot,” at the medial knee and upper medial tibia. Patients with pes anserine bursitis likely will complain of pain on the inside (medial aspect) of the knee, particularly with rising from a seated position, going upstairs, or sitting with their legs crossed. This article focuses on the clinical entity of pes anserine bursitis, unless otherwise specifically stated. Ī more generic term, pes anserine pain syndrome, has been applied to refer to medial knee pain, which may or may not include inflammation of the bursa sac. The pes anserine bursa is sandwiched between the proximal medial tibia and the insertion point of the three tendons. The term “pes anserine” comes from the Latin referring to “goose’s foot,” which the tendinous structures of the semitendinosus, gracilis, and sartorius muscles are said to resemble as they join to insert at the medial knee. Pes anserine bursitis is a clinical entity associated with pain at the medial knee and upper tibial region.
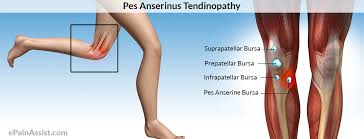
Bursitis is usually accompanied by tenderness however, swelling and redness may also be present. The bursae are the cavitary structures lined with synovial tissue that cushion and assist during the motion of joints and muscles. Bursitis is the general term used to describe inflammation of any bursae.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
